Summary
Modules
Build Your Own
Documentation
Contact
Documentation
The Background of Sybil
This paper was delivered at the 2004 International Computer Music Conference
in Miami and is also published in the Proceedings. It describes the background
to Sybil and explains the concepts behind the software.
PDF
Download![]()
Sybil: a guided tour of some key features
This file is a pdf version (for downloading) of the Sybil Guide
on this website. It contains text and screen shots introducing the Sybil
software.
PDF Download![]() (the full text can also be read below online.)
(the full text can also be read below online.)
This tour uses screenshots to illustrate some of the main features of Sybil. However, since the live sound and live graphics, with which the student can interact, are crucial to Sybil, a static presentation such as this is inevitably limited. The resolution of the screenshots is also restricted and can make reading some of the text difficult. Having followed this tour you might therefore find it helpful to look at the software itself, where the interactivity will become evident.
1. This screenshot is from the very beginning of the first module 'Introduction to Sound Synthesis and Processing'. It shows the navigation tools, permitting users to move between Sections and Pages easily, and the Audio Controls.
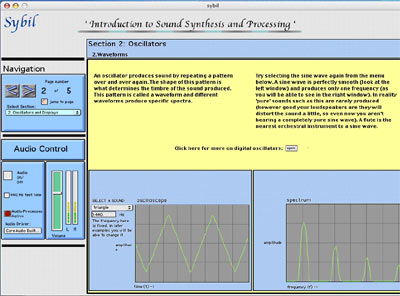
2. Here, the basics of waveforms and their spectral content are introduced. The student can select different waveforms and see both the waveform and the spectrum generated live, along with hearing the sound. Explanatory text is provided. More technical notes can be found, optionally, in a pop-up text box.
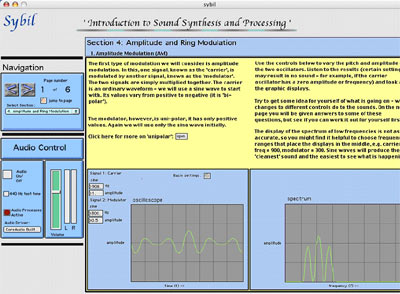
3. On this page the spectral implications of Amplitude Modulation (AM) can be seen, and experimented with live. Changing either the 'carrier' or 'modulation' frequencies has a different effect, which is both audible and visible in the display of the spectrum. Seeing and hearing the results makes the learning experience much more immediate, especially to less-technically oriented students.
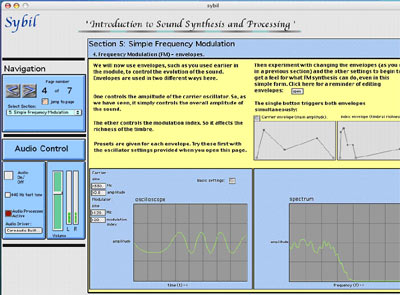
4. Here the dynamic effects of envelopes controlling the evolution of Frequency Modulation over time are presented. The graphic displays, as well as the sound, change as the sound evolves. They show how the amplitude and spectral richness of the sound change according to their respective envelopes. The student may modify the envelopes in order to experiment with different patterns of evolution.
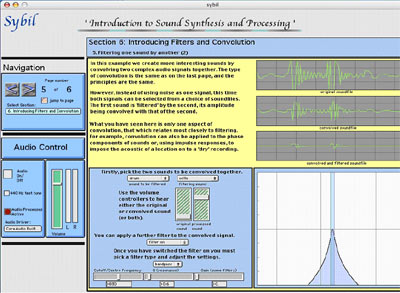
5. This screenshot is taken from late in the module 'Introduction to Sound Synthesis and Processing'. It is not as technical as some of the earlier sections but aims to stimulate students' interest in going further in their exploration of the creative potential of digital sound. Here two sounds (pre-recorded sound files) are selected from menus and the sounds are convolved before being filtered. The original, convolved and filtered signals are all displayed, as is the filter shape.
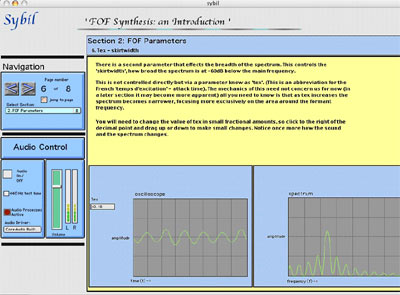
6. This screenshot from early in the more advanced module on 'FOF synthesis: an Introduction' shows the spectrum of the formant region generated by the FOF algorithm. On this page particular page the student is encouraged to experiment with changing the setting of the 'tex' parameter, to see and hear the resulting changes to the spectrum. This is a particularly complex algorithm with many parameters and Sybil provides a much more intuitive and creative approach to learning about it.
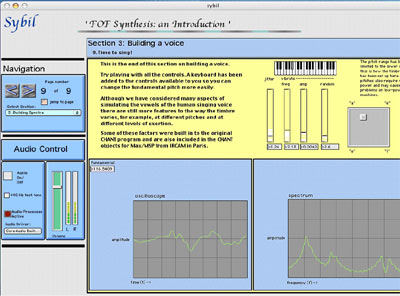
7. This is a screenshot from later in the FOF module. Here a vocal sound has been constructed from five formant regions. Students can experiment to find appropriate settings for vibrato speed and amplitude using on-screen faders, as well as adjusting random elements that add realism. Using their ears as they play with the sound they can learn about what makes for a 'realistic' and satisfying imitation. An on-screen music keyboard can be used to play pitches. The vowel sound can also be changed using a two-dimensional slider. As usual, the signal and spectrum are displayed to give live visual feedback in addition to the sound.
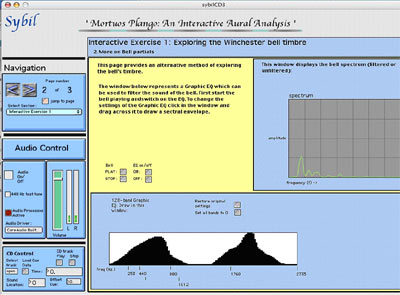
8. Finally, an example from one of the latest developments in Sybil. Here Sybil has been used to create an Interactive Aural Analysis of a piece of electroacoustic music (Jonathan Harvey's Mortuos Plango, Vivos Voco).
In addition to written text, the reader can explore the composition aurally. An additional set of CD controls has been added (bottom left corner), and the user can play back precise sound examples from the work. Live synthesis and processing is also used to re-create some of the techniques used in the composition and so give the reader a greater understanding of the processes used and the compositional choices facing the composer.